Featured Articles
Feature Articles
- Traditional IRAs vs. Roth IRAs
- Tax Tips for Those Affected By Natural Disasters
- Business Entertainment Expenses
- Preparing an Effective Business Plan
- Identity Theft: What to Watch out for and What to do
Tax Tips
- Who Can Represent You Before the IRS?
- Ten Key Tax Facts about Home Sales
- Virtual Currency Treated as Property for Tax Purposes
- Understanding the Gift Tax
- Keep Track of Miscellaneous Deductions
QuickBooks Tips
Two types of IRAs are available to fund your retirement: Traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs. While both are subject to many of the same rules there are several important differences. It’s important to understand these differences because the type of individual retirement account (IRA) you choose can significantly impact your financial future and that of your family.
Who Can Contribute to an IRA?
Any person with income from wages or self-employment can contribute to an IRA (either traditional or Roth)–including children as long as they meet the income conditions. Individuals can contribute up to $5,500 in 2017. A catch-up contribution of $1,000 is allowed for anyone over the age of 50, for a total contribution of $6,500. Contributions are also allowed for stay-at-home spouses (up to $5,500 in 2017) as long as the couple’s wages or self-employment earnings total at least $11,000.
Note: You cannot contribute to a traditional IRA if you are age 70 1/2 or older even if you (or your spouse, if filing jointly) have taxable compensation. You can, however, make contributions to your Roth IRA after you reach age 70 1/2.
Income Limits
A traditional IRA does not have income limits; however, contributions to a Roth IRA might be limited based on your filing status and income.
For example, in 2017, if you file a joint return with your spouse, you cannot contribute to a Roth IRA if your income (AGI or adjusted gross income) is more than $196,000. However, you may be able to contribute a reduced amount if your income is greater than $186,000 but less than $196,000. For income below $186,000, you may contribute up to $5,000 ($6,500 if age 50 or older) or your taxable compensation for the year if your compensation was less than this dollar limit. To figure the reduced amount you can contribute, use the worksheet in Publication 590-A, Contributions to Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs). Please call if you need assistance figuring this out this amount.
Tax Treatment
Taxable Income
Contributions to a traditional IRA are made pre-tax. As such, they lower your taxable income, which could enable you to take advantage of tax breaks you might not otherwise qualify for with a higher income.
Contributions to Roth IRAs are made after-tax (i.e. you’ve already paid the tax) and do not lower your pre-tax income. Unlike a traditional IRA, however, you will owe no tax on income from withdrawals made during your retirement.
Withdrawals before Age 59 1/2
Withdrawals from a traditional IRA that are made before the age of 59 1/2 are subject to an early withdrawal penalty. There are, however, several exemptions that allow you to use the funds but waive the penalty. These include: Using IRA funds to purchase your first home (up to $10,000) and using funds to offset qualified higher education expenses, health insurance premiums while unemployed, and unreimbursed medical expenses in excess of 10 percent AGI.
Withdrawals from Roth IRAs may be taken out penalty and tax-free before age 59 1/2 as long as they are contributions (not earnings). Withdrawals that are earnings are subject to the same 10 percent penalty tax as traditional IRAs. There is an exception for qualified first-time home-buyers: A maximum of $10,000 of Roth IRA earnings may be withdrawn penalty-free to pay for qualified first-time home-buyer expenses as long as at least five tax years have passed since your initial contribution.
Withdrawals after Age 59 1/2
Once you reach age 59 1/2, you may begin taking distributions. While you are not required to take distributions at this age, you must start taking distributions by April 1 following the year in which you turn age 70 1/2 and by December 31 of later years. With a traditional IRA, any deductible contributions and earnings that are withdrawn (typically referred to as distributions when you retire) are considered taxable income. Income from Roth IRA distributions is generally tax-free and unlike a traditional IRA, there is no age requirement for distributions from a Roth IRA.
Questions about IRAs? Don’t hesitate to call.
Every year, hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, wildfires, and other natural disasters affect people throughout the US. The bad news is that recovery efforts after natural disasters can be costly. For instance, when hurricanes strike they not only cause wind damage but can cause widespread flooding. Many homeowners are not covered for damage due to flooding because most standard insurance policies do not cover flood damage. Fortunately, tax relief is available–but only if you meet certain conditions. For business owners and self-employed individuals who may owe estimated taxes, for example, the IRS typically delays filing deadlines for taxpayers who reside or have a business in the disaster area.
Deducting Casualty Losses: Tips for Homeowners
Fortunately, personal casualty losses are deductible on your tax return as long as the property is located in a federally declared disaster zone (please call the office if you are not sure). You must also meet the following four conditions:
Note: Some of the casualty loss rules for business or income property are different than the rules for property held for personal use.
1. The loss was caused by a sudden, unexplained, or unusual event.
Natural disasters such as flooding, hurricanes, tornadoes, and wildfires all qualify as sudden, unexplained, or unusual events.
2. The damages were not covered by insurance.
You can only claim a deduction for casualty losses that are not covered or reimbursed by your insurance company. Keep in mind that timing is important. If you submit a claim to your insurance company late in the year, then your claim might not be processed before it is time to prepare your taxes. One solution is to file for a 6-month extension on your taxes. If you have any questions about this, please call the office.
3. The dollar amount of you losses were greater than the reductions required by the IRS.
To claim casualty losses on your tax forms, the IRS requires several “reductions,” the first of which is referred to as the $100 loss limit and requires taxpayers to subtract $100 from the total loss amount.
Next, you need to reduce the loss amount by 10 percent of your adjusted gross income (AGI). Here is an example: Let’s say your AGI is $35,000 and your insurance company paid for all of the losses except $5,800 that you incurred as a result of tornado damage. First, you would first subtract $100 and then reduce that amount by $3500. The amount you could deduct as a loss would be $2,200.
4. You must itemize.
To claim a deduction for the loss, you must itemize your taxes. If you normally don’t itemize but have a large casualty loss, you can calculate your taxes both ways to figure out which method gives you the lowest tax bill. Please call if you need help figuring out which method is best for your particular circumstances.
Two options for deducting casualty losses on your tax returns.
You can deduct the losses in the year in which they occurred or claim them for the prior year’s return. For example, if you were affected by a natural disaster this year, you can claim your losses on your 2017 tax return or amend your 2016 tax return and deduct your losses. If you choose to deduct losses on your 2016 tax return, then you have one year from the date the tax return was due to file it.
Tip: Do not consider the loss of future profits or income due to the casualty as you figure your loss.
Figuring Amount of Loss
Figure the amount of your loss using the following steps:
- Determine what your adjusted basis in the property was before the casualty occurred. For property you buy, your basis is usually its cost to you. For property you acquire in some other way, such as inheriting it or getting it as a gift, you must figure your basis in another way. Please call the office for more information.
- Determine the decrease in fair market value (FMV) of the property as a result of the casualty. FMV is the price at which you could sell your property to a willing buyer. The decrease in FMV is the difference between the property’s FMV immediately before and immediately after the casualty.
- Subtract any insurance or other reimbursements that you received or expect to receive from the smaller of those two amounts.
Tax Relief for Small Business Owners
Individuals, as well as businesses affected by severe storms, tornadoes, straight-line winds, and flooding in Arkansas and Missouri with an estimated income tax payment originally due on or after April 26, 2017, and before Aug. 31, 2017, will not be subject to penalties for failure to pay estimated tax installments as long as such payments are paid on or before Aug. 31, 2017.
If you have been affected by a natural disaster, please call the office immediately and receive assistance figuring out when your tax payments are due.
Have you been affected by a natural disaster this year? Are you wondering if you qualify for tax relief? Help is just a phone call away.
As a business owner, you are entitled to deduct certain expenses on your tax return such as those relating to entertaining clients. Entertainment is considered any activity that provides entertainment, amusement, or recreation. It may also include meeting the personal, living, or family needs of individuals including providing meals, a hotel suite, or a car to customers or their families.
A meal that you provide to a customer or client may also be considered a form of entertainment. The meal may be part of other entertainment or stand alone. Meal expenses are defined as the cost of food, beverages, taxes, and tips for the meal. To deduct an entertainment-related meal, you or your employee must be present when the food or beverages are provided, and you cannot deduct a meal as both a travel and entertainment expense.
Limits and Restrictions
Entertainment expenses are generally deductible at 50 percent. Entertainment costs, taxes, tips, cover charges, room rentals, maids, and waiters are all subject to the 50 percent limit on entertainment deductions.
Entertainment expenses are also subject to certain limits and restrictions such as whether they qualify as “ordinary and necessary” and not “lavish or extravagant.” They must also be directly related to or associated with, your business and you must keep detailed records substantiating your expenses (more on this below). Furthermore, the person you entertained must be a business associate; that is, someone who could reasonably be expected to be a customer or conduct business with you such as an employee, client, or professional advisor.
If it is customary to entertain a business associate with his or her spouse and your spouse also attends, entertainment expenses for both spouses are deductible, thanks to something called the “closely connected rule.” For more information about this topic, please contact the office.
Note: If you are an employee who is reimbursed in full by your employer different tax rules apply (e.g. you are not subject to the deduction limits).
Location must be Conducive to Business
Your Home
Entertainment expenses are only deductible when they take place in a location conducive to business. A nightclub or theater is not considered a place conducive to business, but your home is. For example, if you hold a small (less than 12 people) party for clients and business associates at your home during the summer it may be deductible as long as you discussed business with your guests. The amount of time that business was discussed is not significant.
Year-end parties for employees, as well as sales seminars and presentations held at your home, are generally 100 percent deductible provided costs for food and refreshments are reasonable and not lavish.
Entertainment Facilities
Out-of-pocket expenses for food and beverages, catering, gas, and fishing bait provided at facilities you own or are a member of such as a yacht, hunting lodge, fishing camp, swimming pool, and tennis court are deductible subject to entertainment expense limitation of 50 percent. However, you may not deduct expenses related to the depreciation and upkeep of the facility or for rent and utilities.
Note: Dues paid to country clubs, social, or golf and athletic clubs are not deductible.
Skybox
If you rent a skybox or other private luxury box for more than one event at the same sports arena, you generally can’t deduct more than the price of a nonluxury box seat ticket. You can, however, count each game as one event. Deduction for those seats is then subject to the 50 percent entertainment expense limit. If the cost of food and beverages are on a separate receipt, you are allowed to deduct those expenses (as long as they are reasonable) in addition to the amounts allowable for the skybox, subject of course, to the requirements and limits that apply.
Expenses must be “Directly Related” or “Associated With”
Expenses are directly related if you can show that there was more than a general expectation of gaining some business benefit, rather than simply goodwill. In addition, you must show that you conducted business during the entertainment and that the active conduct of business was your main purpose.
Even if you cannot show that the entertainment was “directly related” you may still be able to deduct the expenses as long as you can prove the entertainment was “associated with” your business. To meet this test, you must have had a clear business purpose when you took on the expense, and the entertainment must directly precede or come after a substantial business discussion.
Substantiating your Expenses
Tax law requires you to keep records that will prove the business purpose and amounts of your business entertainment as well as other business expenses. The most frequent reason that the IRS disallows entertainment expenses is the failure to show the place and business purpose of an item. Therefore it is paramount that you keep excellent records.
To substantiate entertainment expenses you must show the following:
- The amount of each separate expense.
- The date, time, place, and type of entertainment (e.g. dinner).
- The business purpose and nature of any business discussion that took place.
- The business relationship and the name, title, and occupation of the person or people you entertained.
Don’t Miss Out
Tax law is complicated, and this article only touches on a few of the deductions for entertainment expenses you might be entitled to. If you have any questions about entertainment expenses or need assistance setting up a recordkeeping system to document your business-related activities, don’t hesitate to call.
Whether you’re starting a new company, seeking additional financing for an existing one, or analyzing a new market, a business plan is a valuable tool. Think of it as your blueprint for success. Not only will it clarify your business vision and goals, but it will also force you to gain a thorough understanding of how resources (financial and human) will be used to carry out that vision and goals.
Before you begin preparing your business plan, take the time to carefully evaluate your business and personal goals as this may give you valuable insight into your specific goals and what you want to accomplish. Think about the reasons why you are starting a new business; maybe you’re ready to be your own boss, or you want financial independence. Whatever the reason it is important to determine the “why.”
Next, you need to figure out what business is “right for you.” Chances are you already have a specific business in mind but if not you might want to think about your business in terms of what technical skills and experience you have, whether you have any marketable hobbies or interests, what competition you might have, how you might market your products or services, and how much time you have to run a successful business (it may take more time than you think).
Finally, you’ll need to figure out how you want to get started. Most people choose one of three options: starting a business from scratch, purchasing an existing business, or operating a franchise. Each has pros and cons, and only you can decide which business fits.
Pre-Business Checklist
The final step before developing your plan is developing a pre-business checklist which might include:
- Business legal structure
- Accounting or bookkeeping system
- Insurance coverage
- Equipment or supplies
- Compensation
- Financing (if any)
- Business location
- Business name
Based on your initial answers to the items listed above, your next step is to formulate a focused, well-researched business plan that outlines your business mission and goals, how you intend to achieve your mission and goals, products or services to be provided, and a detailed analysis of your market. Last, but not least, it should include a formal financial plan.
Preparing an Effective Business Plan
Now, let’s take a look at the components of an effective business plan. Keep in mind that this is a general guideline, and any plan you prepare should be adapted to your specific business with the help of a financial professional.
Introduction and Mission Statement
In the introductory section of your business plan, you should make sure you write a detailed description of your business and its goals, as well as ownership. You can also list skills and experience that you or your business partners bring to the business. And finally, include a discussion of what advantages you and your business have over your competition.
Products, Services, and Markets
In this section, you will need to describe the location and size of your business, as well as your products and/or services. You should identify your target market and customer demand for your product or service and develop a marketing plan is. You should also discuss why your product or service is unique and what type of pricing strategy you will be using.
Financial Management
This section is where you should discuss the financial aspects of your business–and where the advice of a financial professional is vital. The following financial aspects of your business should be discussed in detail:
- Source and amount of initial equity capital.
- Monthly operating budget for the first year.
- Expected return on investment (ROI) and a monthly cash flow for the first year.
- Projected income statements and balance sheets for a two-year period.
- A discussion of your break-even point.
- Explanation of your personal balance sheet and method of compensation.
- Who will maintain your accounting records and how they will be kept.
- Provide “what if” statements that address alternative approaches to any problem that may develop.
Business Operations
The Business Operations section generally includes an explanation of how the business will be managed on a day-to-day basis and discusses hiring and personnel procedures (HR), insurance and lease or rent agreements, and any other pertinent issues that could affect your business operations. In this section, you should also specify any equipment necessary to produce your product or services as well as how the product or service will be produced and delivered.
Concluding Statement
The concluding statement should summarize your business goals and objectives and express your commitment to the success of your business.
Questions?
If you have any questions about business plans or need assistance creating one, please contact the office.
Tax-related identity theft typically occurs when someone uses your stolen Social Security number to file a tax return claiming a fraudulent refund. Anyone can fall victim to identity theft. Here is an important reminder of how to protect yourself from identity theft, what to watch out for, and what do if your identity has been compromised:
1. Protect your Records. Do not carry your Social Security card with you, or any other documents with your Social Security Number (SSN) on them. Only provide your SSN if it is completely necessary and you know the person requesting it. Routinely change passwords for all of your Internet accounts and protect your personal information at home and protect your computers with anti-spam and anti-virus software.
2. Don’t Fall for Scams. Criminals often try to impersonate your bank, credit card company, and even the IRS in order to steal your personal data. Learn to recognize and avoid those fake emails and texts.
3. Beware of Threatening Phone Calls. The IRS will never call you threatening a lawsuit or arrest, or to demand an immediate tax payment using a prepaid debit card, gift card, or wire transfer. Generally, if you owe taxes, the IRS will first mail a bill to the taxpayer. Furthermore, The IRS initiates most contacts through regular mail delivered by the United States Postal Service. While there are certain circumstances when the IRS will visit your home or business, taxpayers will generally first receive several letters (called “notices “) from the IRS in the mail beforehand. The IRS will also not:
- Demand that you pay taxes without the opportunity to question or appeal the amount they say you owe. You should also be advised of your rights as a taxpayer.
- Threaten to bring in local police, immigration officers or other law-enforcement to have you arrested for not paying. The IRS also cannot revoke your driver’s license, business licenses, or immigration status. Threats like these are common tactics scam artists use to trick victims into buying into their schemes.
4. Report ID Theft to Law Enforcement. If you discover that you cannot e-file your return because a tax return already was filed using your SSN, please call the office immediately for assistance. Next, you will generally need to take the following steps:
- File your taxes by paper and pay any taxes owed.
- File an IRS Form 14039, Identity Theft Affidavit.
- File a complaint report with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
- Contact one of the three credit bureaus (Equifax, TransUnion, or Experian), to place a fraud alert or credit freeze on your account.
5. Complete an IRS Form 14039 Identity Theft Affidavit. File IRS Form 14039, Identity Theft Affidavit. Print out the form and mail or fax it according to the instructions. Continue to pay your taxes and file your tax return, even if you must do so by filing on paper.
6. IRS Notices and Letters. If the IRS identifies a suspicious tax return with your social security number on it, they may send you a letter asking you to verify your identity and will provide instructions on how to do so. You may need to call a special phone number or visit a Taxpayer Assistance Center. This is to protect you from tax-related identity theft.
7. IP PINs. If a taxpayer reports that they are a victim of ID theft or the IRS identifies a taxpayer as being a victim, he or she will be issued an IP PIN. The IP PIN is a unique six-digit number that a victim of ID theft uses to file a tax return. Each year, you will receive an IRS letter with a new IP PIN.
8. Data Breaches. If you learn about a data breach that may have compromised your personal information, keep in mind that not every data breach results in identity theft. Furthermore, not every identity theft case involves taxes. Make sure you know what kind of information has been stolen so you can take the appropriate steps before contacting the IRS.
9. Report Suspicious Activity. If you suspect or know of an individual or business that is committing tax fraud, you can report it on the IRS.gov website.
10. IRS Website. Information about identity theft is available on the IRS website. There is also a special section devoted to identity theft with a phone number available for victims to obtain assistance.
If you have any questions about identity theft or have any reason to believe that you’ve been a victim of identity theft, please contact the office as soon as possible.
Many people use a tax professional to prepare their taxes. Anyone who prepares, or assists in preparing, all or substantially all of a federal tax return for compensation is required to have a valid Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN). All enrolled agents must also have a valid PTIN. Tax professionals with an IRS Preparer. If you choose to have someone prepare your federal tax return you should know who can represent you before the IRS–and when–if there is a problem with your return.
Representation rights, also known as practice rights, fall into two categories:
- Unlimited Representation
- Limited Representation
Unlimited representation rights allow a credentialed tax practitioner to represent you before the IRS on any tax matter. This is true no matter who prepared your return. Credentialed tax professionals who have unlimited representation rights include:
- Enrolled agents
- Certified Public Accountants
- Attorneys
Limited representation rights authorize the tax professional to represent you if, and only if, they prepared and signed the return. They can do this only before IRS revenue agents, customer service representatives and similar IRS employees. They cannot represent clients whose returns they did not prepare. They cannot represent clients regarding appeals or collection issues even if they did prepare the return in question.
For returns filed after December 31, 2015, the only tax return preparers with limited representation rights are Annual Filing Season Program Participants. The Annual Filing Season Program is a voluntary program. Non-credentialed tax return preparers who aim for a higher level of professionalism are encouraged to participate.
Other tax return preparers have limited representation rights, but only for returns filed before Jan. 1, 2016. Keep these changes in mind and choose wisely when you select a tax return preparer.
In most cases, gains from sales are taxable. But did you know that if you sell your home, you may not have to pay taxes? Here are ten facts to keep in mind if you sell your home this year.
1. Exclusion of Gain. You may be able to exclude part or all of the gain from the sale of your home. This rule may apply if you meet the eligibility test. Parts of the test involve your ownership and use of the home. You must have owned and used it as your main home for at least two out of the five years before the date of sale.
2. Exceptions May Apply. There are exceptions to the ownership, use, and other rules. One exception applies to persons with a disability. Another applies to certain members of the military. That rule includes certain government and Peace Corps workers. For more information about these exceptions, please call the office.
3. Exclusion Limit. The most gain you can exclude from tax is $250,000. This limit is $500,000 for joint returns. The Net Investment Income Tax will not apply to the excluded gain.
4. May Not Need to Report Sale. If the gain is not taxable, you may not need to report the sale to the IRS on your tax return.
5. When You Must Report the Sale. You must report the sale on your tax return if you can’t exclude all or part of the gain. You must report the sale if you choose not to claim the exclusion. That’s also true if you get Form 1099-S, Proceeds From Real Estate Transactions.
6. Exclusion Frequency Limit. Generally, you may exclude the gain from the sale of your main home only once every two years. Some exceptions may apply to this rule.
7. Only a Main Home Qualifies. If you own more than one home, you may only exclude the gain on the sale of your main home. Your main home usually is the home that you live in most of the time.
8. First-time Homebuyer Credit. If you claimed the first-time homebuyer credit when you bought the home, special rules apply to the sale. For more on those rules, please call.
9. Home Sold at a Loss. If you sell your main home at a loss, you can’t deduct the loss on your tax return.
10. Report Your Address Change. After you sell your home and move, update your address with the IRS. To do this, file Form 8822, Change of Address. You can find the address to send it to in the form’s instructions on page two. If you purchase health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace, you should also notify the Marketplace when you move out of the area covered by your current Marketplace plan.
Questions? Help is just a phone call away.
Many retailers and online businesses now accept virtual currency for sales transactions but the federal tax implications remain relatively unknown to many retailers. If you’re a retailer who accepts virtual currency such as Bitcoins for transactions, here’s what you need to know.
Sometimes, virtual currency such as Bitcoins operate like “real” currency, i.e. the coin and paper money of the United States or of any other country that is designated as legal tender, circulates, and is customarily used and accepted as a medium of exchange in the country of issuance.
But bitcoins do not have legal tender status in any jurisdiction. If you’ve been paid in virtual currency, you should be aware that virtual currency is treated as property for U.S. federal tax purposes. In other words, general tax principles that apply to property transactions also apply to transactions using virtual currency. Among other things, this means that:
- Wages paid to employees using virtual currency are taxable to the employee, must be reported by an employer on a Form W-2, and are subject to federal income tax withholding and payroll taxes.
- Payments using virtual currency made to independent contractors and other service providers are taxable, and self-employment tax rules generally apply. Normally, payers must issue Form 1099.
- The character of gain or loss from the sale or exchange of virtual currency depends on whether the virtual currency is a capital asset in the hands of the taxpayer.
- A payment made using virtual currency is subject to information reporting to the same extent as any other payment made in property.
If you’re a business or individual with questions about virtual currency such as bitcoins, don’t hesitate to call the office for assistance.
If you gave money or property to someone as a gift, you may wonder about the federal gift tax. Many gifts are not subject to the gift tax. Here are seven tax tips about gifts and the gift tax.
1. Nontaxable Gifts. The general rule is that any gift is a taxable gift. However, there are exceptions to this rule. The following are not taxable gifts:
- Gifts that do not exceed the annual exclusion for the calendar year,
- Tuition or medical expenses you paid directly to a medical or educational institution for someone,
- Gifts to your spouse (for federal tax purposes, the term “spouse” includes individuals of the same sex who are lawfully married),
- Gifts to a political organization for its use, and
- Gifts to charities.
2. Annual Exclusion. Most gifts are not subject to the gift tax. For example, there is usually no tax if you make a gift to your spouse or to a charity. If you give a gift to someone else, the gift tax usually does not apply until the value of the gift exceeds the annual exclusion for the year. For 2017, the annual exclusion is $14,000 (same as 2016).
3. No Tax on Recipient. Generally, the person who receives your gift will not have to pay a federal gift tax. That person also does not pay income tax on the value of the gift received.
4. Gifts Not Deductible. Making a gift does not ordinarily affect your federal income tax. You cannot deduct the value of gifts you make (other than deductible charitable contributions).
5. Forgiven and Certain Loans. The gift tax may also apply when you forgive a debt or make a loan that is interest-free or below the market interest rate.
6. Gift-Splitting. In 2017, you and your spouse can give a gift up to $28,000 ($14,000 each) to a third party without making it a taxable gift. You can consider that one-half of the gift be given by you and one-half by your spouse.
7. Filing Requirement. You must file Form 709, United States Gift (and Generation-Skipping Transfer) Tax Return if any of the following apply:
- You gave gifts to at least one person (other than your spouse) that amount to more than the annual exclusion for the year.
- You and your spouse are splitting a gift. This is true even if half of the split gift is less than the annual exclusion.
- You gave someone (other than your spouse) a gift of a future interest that they can’t actually possess, enjoy, or from which they’ll receive income later.
- You gave your spouse an interest in property that will terminate due to a future event.
Still confused about the gift tax? Please call for assistance.
Miscellaneous deductions such as certain work-related expenses you paid for as an employee can reduce your tax bill, but you must itemize deductions when you file to claim these costs. If you usually claim the standard deduction, think about itemizing instead because you might be able to pay less tax. Here are some tax tips that may help you reduce your taxes:
Deductions Subject to the Limit. You can deduct most miscellaneous costs only if their sum is more than two percent of your adjusted gross income. These include expenses such as,
- Unreimbursed employee expenses.
- Job search costs for a new job in the same line of work.
- Some work clothes and uniforms.
- Tools for your job.
- Union dues.
- Work-related travel and transportation.
- The cost you paid to prepare your tax return. These fees include the cost you paid for tax preparation software. They also include any fee you paid for e-filing of your return.
Deductions Not Subject to the Limit. Some deductions are not subject to the two percent limit. They include:
- Certain casualty and theft losses. In most cases, this rule applies to damaged or stolen property you held for investment. This may include personal property such as works of art, stocks, and bonds.
- Gambling losses up to the total of your gambling winnings.
- Losses from Ponzi-type investment schemes.
You claim allowable miscellaneous deductions on Schedule A, Itemized Deductions, but keep in mind, however, that there are many expenses that you cannot deduct. For example, you can’t deduct personal living or family expenses.
Need more information about itemizing deductions or help setting up a system to track your itemized deductions? Don’t hesitate to call.
“I don’t write checks anymore.” You hear a lot of people say that these days, and for many consumers, debit cards, smartphone payment apps, and online banking have all replaced the old paper checkbook.
That’s fine if you’re at Starbucks or the grocery store, but many small businesses still prefer to issue paper checks to pay bills, cover expenses, and make product and service purchases. QuickBooks provides tools that help you create, print, and track checks.
But you don’t just head to the Write Checks window every time something needs to be paid. There are numerous times when you would record a payment in a different area of the program. For example, if you’ve already created a bill in Enter Bills, you’d go to the Pay Bills screen to dispatch a check.
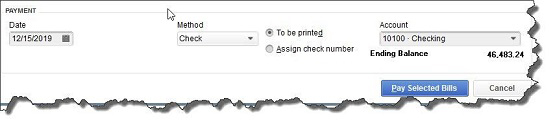
Figure 1: Once you’ve recorded a bill in Enter Bills, you need to visit the Pay Bills screen to dispatch a check. The image above shows the bottom of that screen.
Other examples here include:
- Issuing paychecks (click the Pay Employees icon),
- Submitting payroll taxes and liabilities (Pay Liabilities icon), and
- Paying sales taxes (Manage sales tax icon).
Simple Steps
Let’s say you asked an employee to go to an office supply store to pick up some copy paper because you ran short before your normal shipment came in. If you knew the exact amount it would cost, you could write a check directly to the shop. But the employee agrees to pay for it and be reimbursed.
Click the Write Checks icon on the home page. If the BANK ACCOUNT that’s showing isn’t the correct one, click the arrow to the right of that field and select the right one. Unless you’ve written a check to that employee before, he won’t be in the Vendor list that opens when you click the arrow to the right of PAY TO THE ORDER OF. Enter his name in that field.
The Name Not Found window opens. If this was a new vendor that you would be working with again, you’d click Set Up and follow the instructions in the step-by-step wizard that opened. Since this isn’t the case, click Quick Add. In the window that opens, click the button next to Vendor.
Note: If you’re using a payroll application, you already have an employee record for that individual, which would have filled in automatically when you started typing the name. Since this is a Non-Payroll Transaction, it won’t get mixed up with his payroll records as long as you assign the correct account.
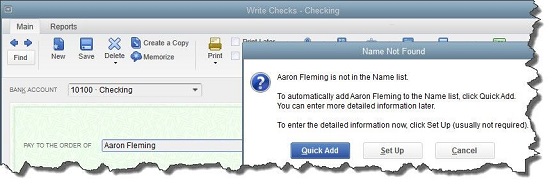
Figure 2: If you don’t want to create an entire record for the payee of a check, you can just click Quick Add.
QuickBooks will then return you to the check-writing screen, where you can verify the check number and date, and enter the amount. Fill in the MEMO field so you’ll remember the reason for the payment.
At the bottom of the screen, you’ll see a tabbed register. The Expenses tab should be highlighted and the amount of your check entered. Click the down arrow in the field under ACCOUNT to open the list, and select Office Supplies. The AMOUNT should fill in automatically. Not sure which account to select, and what the remaining three columns mean? Please call the office for assistance.
Note: You would only enter the expense under the Items tab if you were buying inventory items or paying job-related costs.
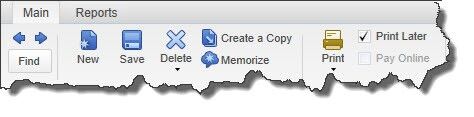
Figure 3: Warning: If you’re planning to print the check, be sure to check the Print Later box in the horizontal toolbar at the top of the screen.
When you’re finished, save the transaction. Since you want to pay the employee right away, click the Print Checks icon and click in the field in front of the correct check to select it, then click OK.
Easy, But Tricky
QuickBooks makes the mechanics of writing checks easy. Simple as it is, though, a lot can go wrong if you, for example:
- Issue a check from the wrong screen,
- Classify a check incorrectly, or,
- Skip a step.
If you’re new to check-writing in QuickBooks or are confused about any of its attributes, don’t hesitate to contact the office to set up a learning session with one of our QuickBooks professionals.
Next Article
Tax Due Dates for August 2017
August 10
Employees Who Work for Tips – If you received $20 or more in tips during July, report them to your employer. You can use Form 4070.
Employers – Social Security, Medicare, and withheld income tax. File Form 941 for the second quarter of 2017. This due date applies only if you deposited the tax for the quarter in full and on time.
August 15
Employers – Nonpayroll withholding. If the monthly deposit rule applies, deposit the tax for payments in July.
Employers – Social Security, Medicare, and withheld income tax. If the monthly deposit rule applies, deposit the tax for payments in July.
Copyright © 2017 All materials contained in this document are protected by U.S. and international copyright laws. All other trade names, trademarks, registered trademarks and service marks are the property of their respective owners.
